Understanding the Plant-Based Diet: Key Components and Foods
Introduction to Plant-Based Diets
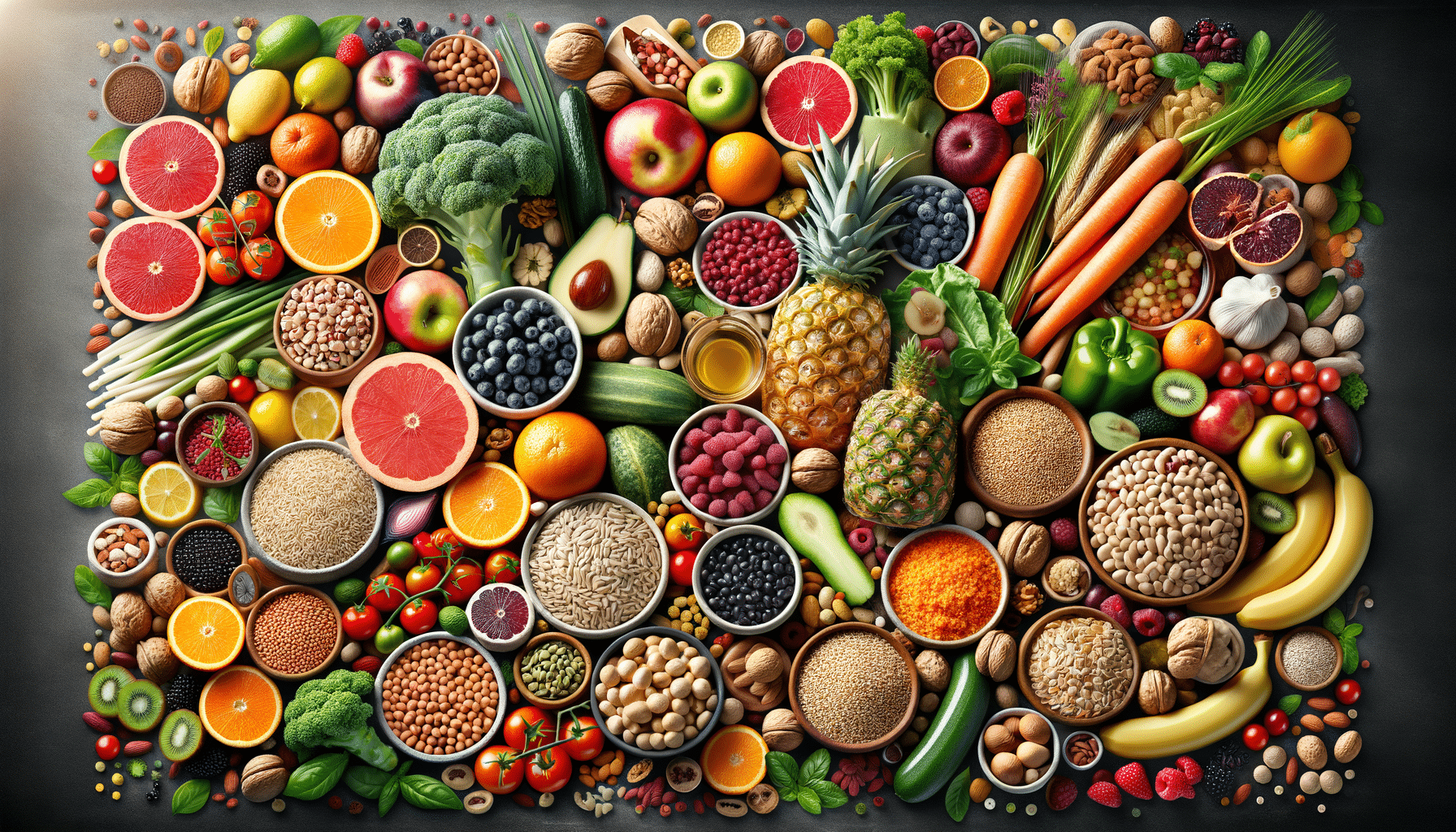
The plant-based diet has gained significant popularity in recent years, driven by growing awareness of health, environmental, and ethical concerns. This dietary approach emphasizes foods primarily derived from plants, including fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Unlike strict vegetarian or vegan diets, a plant-based diet allows for occasional consumption of animal products, but the focus remains on plant-derived foods. This flexibility makes it an attractive option for individuals seeking to improve their health while still enjoying a varied diet.
One of the key benefits of a plant-based diet is its potential to enhance overall health. Numerous studies have highlighted its association with lower risks of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Additionally, plant-based diets tend to be rich in essential nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants, all of which contribute to improved well-being. As more people become aware of these benefits, the plant-based diet continues to gain traction as a sustainable and health-conscious lifestyle choice.
Nutritional Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet
Adopting a plant-based diet can provide a plethora of nutritional benefits, making it a compelling choice for health-conscious individuals. This dietary approach is naturally high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, while being low in saturated fats and cholesterol. Such a nutrient profile is instrumental in maintaining optimal health and preventing chronic diseases.
Key components of a plant-based diet include:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, these foods support immune function and reduce inflammation.
- Whole Grains: Sources of complex carbohydrates and fiber, whole grains promote digestive health and provide sustained energy.
- Legumes: High in protein and fiber, legumes are excellent for heart health and blood sugar regulation.
- Nuts and Seeds: Packed with healthy fats, protein, and micronutrients, they contribute to heart and brain health.
By focusing on these plant-based foods, individuals can achieve a well-rounded and nutrient-dense diet that supports long-term health and vitality.
Environmental Impact of Plant-Based Eating
The environmental benefits of a plant-based diet are substantial, making it an ethical choice for those concerned about sustainability. Livestock farming is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution. By reducing reliance on animal products, individuals can significantly lower their carbon footprint and contribute to environmental preservation.
Some key environmental advantages of plant-based diets include:
- Reduced Carbon Emissions: Plant-based foods require fewer resources and emit less greenhouse gases compared to animal agriculture.
- Conservation of Water: Plant-based diets use significantly less water, as animal agriculture is water-intensive.
- Preservation of Biodiversity: Reducing demand for animal products can help protect habitats and prevent deforestation.
By choosing plant-based foods, individuals not only improve their health but also play a part in promoting a more sustainable and eco-friendly world.
Transitioning to a Plant-Based Diet
For those considering a shift to a plant-based diet, the transition can be both rewarding and challenging. It’s essential to approach this change gradually, allowing time to adapt and explore new foods and recipes. Here are some practical tips to ease the transition:
- Start Small: Begin by incorporating more plant-based meals into your weekly routine, such as “Meatless Mondays.”
- Experiment with New Foods: Explore different fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes to diversify your diet.
- Plan Balanced Meals: Ensure your meals are nutritionally balanced by including a variety of food groups.
- Seek Support: Join plant-based communities or groups for inspiration and guidance.
By taking these steps, individuals can smoothly transition to a plant-based diet, reaping its numerous health and environmental benefits while enjoying a diverse and flavorful culinary experience.
Common Misconceptions and Challenges
Despite its benefits, the plant-based diet is often surrounded by misconceptions and challenges that can deter individuals from adopting it. One common misconception is that plant-based diets lack sufficient protein. However, with careful planning, it’s possible to obtain all essential amino acids from plant sources such as beans, lentils, quinoa, and tofu.
Another challenge is the perception that plant-based diets are expensive. While some specialty products can be costly, staples like grains, legumes, and seasonal produce are often budget-friendly. Planning meals and buying in bulk can further reduce costs.
Lastly, social situations can pose challenges for those on a plant-based diet. Navigating family gatherings or dining out may require extra effort to ensure plant-based options are available. Communicating dietary preferences and suggesting plant-based dishes can help mitigate these challenges.
Understanding and addressing these misconceptions and challenges can empower individuals to embrace a plant-based diet confidently, enjoying its many benefits while overcoming potential obstacles.